Solutions
Horse Construction offers full range of structural strengthening materials with technical supports, documentation supports, products supports, project supports.
Strategic Use of Epoxy Crack Injection: When It Works and When to Avoid It
Epoxy crack injection is a widely used concrete repair method that restores structural integrity by bonding cracked surfaces. However, its effectiveness depends heavily on the nature of the crack and the environmental conditions. This article explores the optimal applications of epoxy injection.
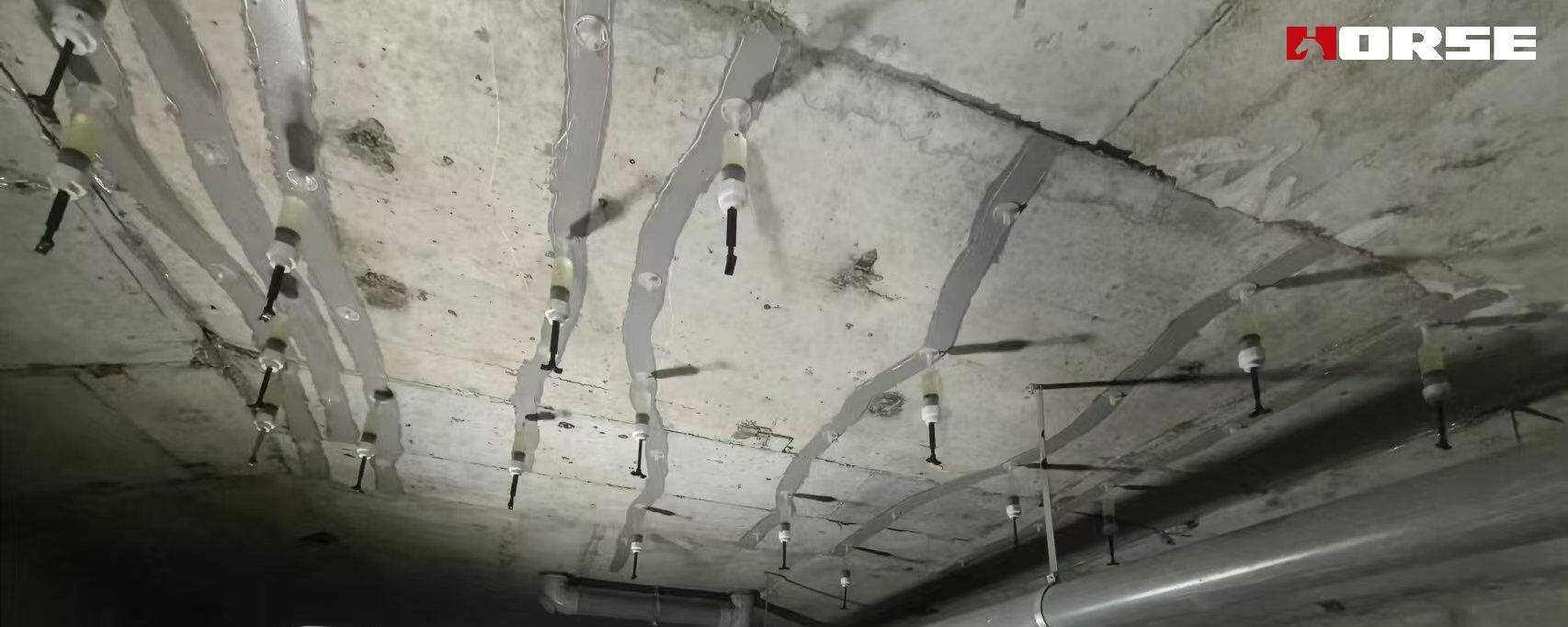

Epoxy excels in repairing static cracks—those that have stabilized and show no further movement. These typically include:
Shrinkage cracks from initial concrete curing
Load-induced cracks where structural movement has ceased
Hairline cracks (<0.3mm) that do not experience dynamic stress
Why it works: Epoxy’s rigid bond restores monolithic behavior, effectively transferring loads across the crack.
Epoxy is ideal when structural continuity must be reestablished, such as in:
Beam, column, and slab cracks in buildings and bridges
Precast concrete connections needing load transfer
Post-tensioned concrete where cracks compromise tendon protection
Performance benefit: Epoxy can achieve compressive strengths exceeding 10,000 psi, often stronger than the surrounding concrete.
Epoxy bonds best in dry conditions, making it suitable for:
Indoor structures (parking garages, industrial floors)
Protected environments (sealed basements, roof slabs)
Pre-dried cracks (using heat or desiccants before injection)
Key consideration: If moisture is present, hydrophobic epoxies or pre-injection drying may be required.
Epoxy’s low viscosity allows it to penetrate fine cracks (as small as 0.05mm), making it ideal for:
Aerospace & nuclear facilities where tight tolerances matter
Marine structures (if properly formulated for chloride resistance)
Historical restoration where minimal invasiveness is required
Epoxy’s rigidity makes it unsuitable for cracks that:
Cycle thermally (expansion/contraction due to temperature changes)
Experience live loads (bridge decks, industrial floors under vibration)
Result from ongoing settlement
Alternative: Polyurethane injection (flexible) or elastomeric sealants (for joints).
If water infiltration is present:
Epoxy will not bond properly to wet surfaces
Hydrostatic pressure can force epoxy out before curing
Freeze-thaw cycles may reopen the crack
Alternative: Hydrophilic or hydrophobic polyurethane, which expands in water.
Cracks caused by:
Differential settlement
Seismic activity
Expansion/contraction cycles
Alternative: Routing and sealing with flexible sealants or installing expansion joints.
Epoxy is a symptomatic fix, not a cure for:
Foundation settlement (needs underpinning or piers)
Corrosion-induced cracking (requires rebar treatment)
Poor structural design (demands load redistribution)
Best practice: Always investigate the cause before selecting a repair method.
Epoxy crack injection is a powerful tool for restoring strength in static, dry, structurally critical cracks. However, it fails when used on moving, wet, or improperly diagnosed cracks.
You can find anything here you are in need of, have a trust trying on these products, you will find the big difference after that.

High strength crack sealing repairing adhesive for the fracture surface of concrete crack

Very strong penetration and low viscosity epoxy crack injection adhesive for repairing concrete crack